Newborn Screening and Diagnosis of Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency (LAL-D)
NEWBORN SCREENING AND LAL-D
Early diagnosis saves lives.
Newborn screening is a fundamental tool for detecting rare diseases such as Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency (LAL-D) from the very first days of life. For babies with Wolman Disease — the most severe form of LAL-D — early detection can be a matter of life or death: without timely intervention, the disease is often fatal before six months of age.

Our organization works to ensure that LAL-D is included in newborn screening programs across Europe. Detecting affected babies early allows families to access life-changing treatment and specialized care from the very beginning.
We are actively involved in the European rare disease community, collaborating with EURORDIS on newborn screening initiatives and contributing to the Screen4Care project.
Through these partnerships, we aim to advance policies, share knowledge, and raise awareness so that every newborn has the opportunity for early diagnosis and a better quality of life.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency is based on two fundamental steps:
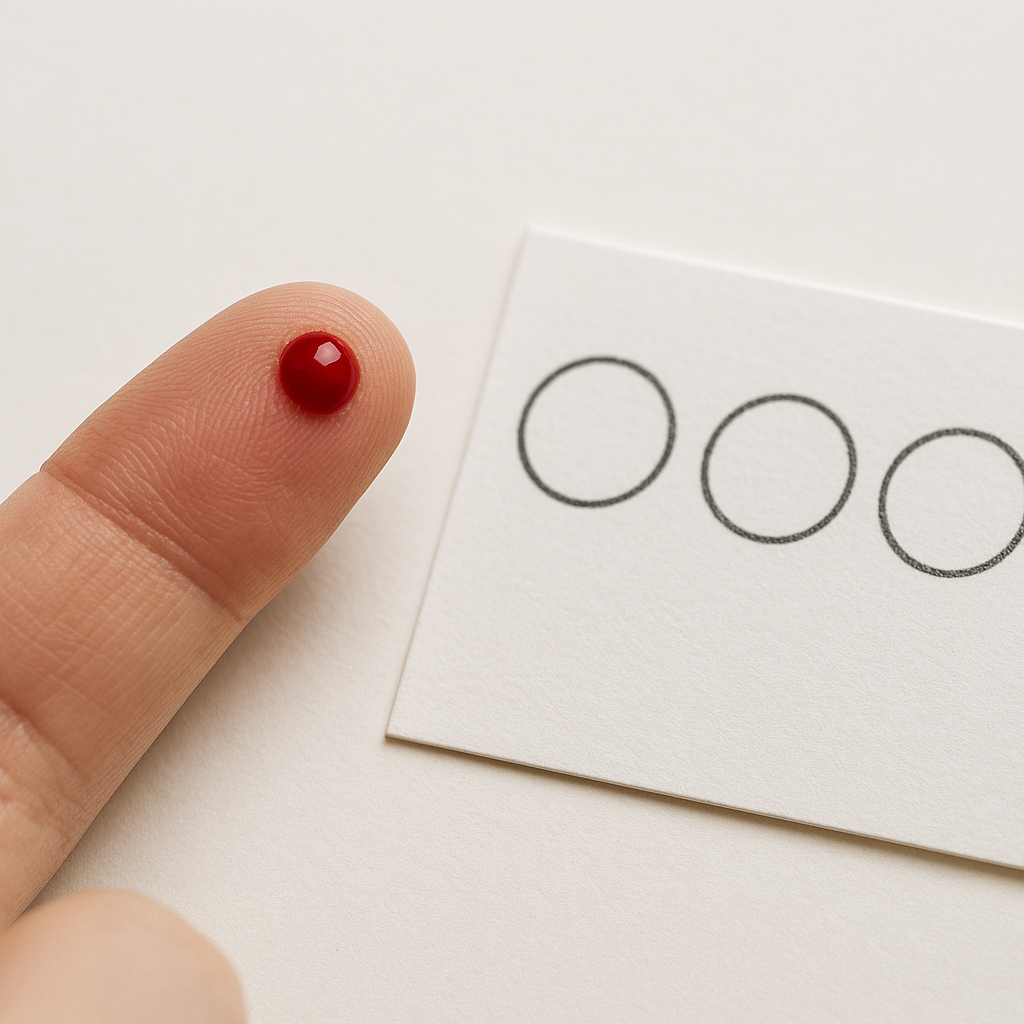 1. Enzyme Activity Test
1. Enzyme Activity Test
The activity of lysosomal acid lipase is measured in leukocytes or in dried blood spots (DBS).
A significantly reduced enzymatic activity confirms the clinical suspicion and helps differentiate LAL-D from other metabolic disorders.

2. Genetic Study
Once the enzymatic deficiency is detected, sequencing of the LIPA gene is performed, which is responsible for producing lysosomal acid lipase.
This analysis confirms the diagnosis and identifies the specific mutation.
Importance of Genetic Testing
It is essential to identify all individuals who carry the genetic mutation within the family branch of diagnosed patients, in order to provide appropriate genetic counseling and prevent transmission of the disease.
To ensure quality and consistency, all samples are sent and centralized at the Foundation for the Study and Therapy of Gaucher Disease and Other Lysosomal Disorders (FEETEG), an entity specialized in lysosomal diseases.
FEETEG is responsible for performing the corresponding studies and, once completed, sends the report directly to the physician who submitted the samples, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with current regulations.
Procedure for Sample Collection and Shipment
- Peripheral blood extraction: volume between 10 and 20 mL
- Tube type: EDTA (purple cap)
- Shipping conditions: room temperature, no refrigeration or freezing. Secure packaging and urgent transport according to current regulations are recommended.
Shipping address:
FEETEG (Foundation for the Study and Therapy of Gaucher Disease and Other Lysosomal Disorders)
C/ Carrera del sábado nº 4, local (Edificio Europa), 50006 Zaragoza, Spain
Phone: +34 976 46 80 41 – Mobile: +34 651 00 83 62
Email: feeteg@fehha.org
Additionally, affected individuals and their families who wish to do so may go directly to the FEETEG laboratory to provide the sample on-site and thus complete this study.